Winform中实现窗体控件适配(自适应窗体)布局_通过C#代码方式
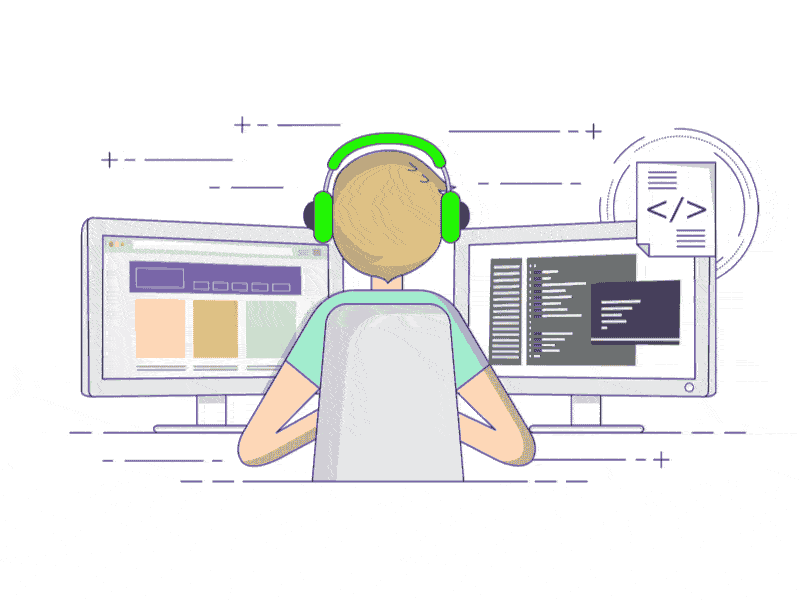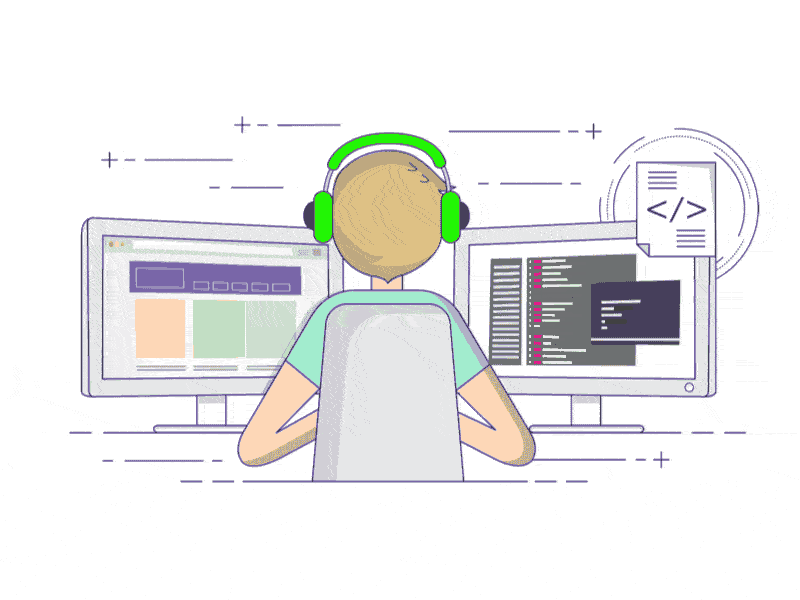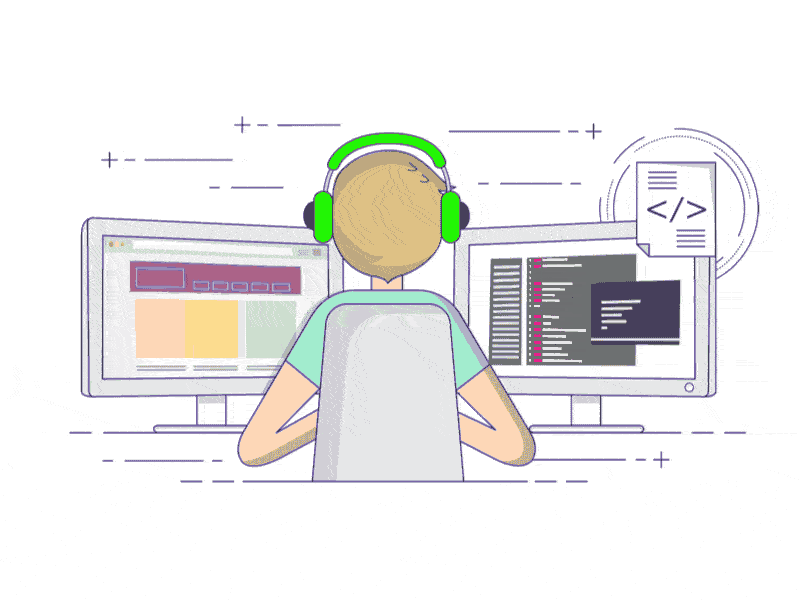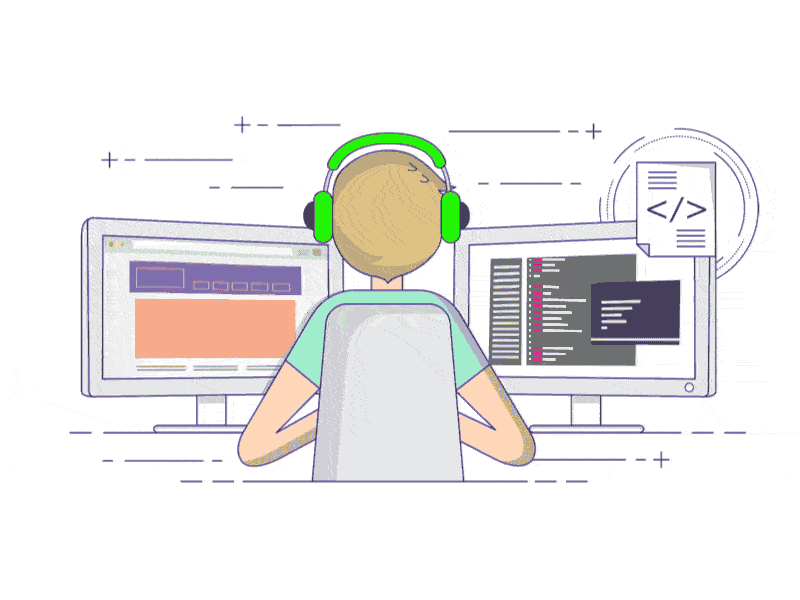
1.1、未启用控件缩放的实现效果
即:未启用控件缩放效果代码时,控件内容都是固定在窗体界面的指定位置,不会跟随窗体的拉伸,放大而进行适配,如下图所示
1.2、启用控件缩放的实现效果
即:启用控件缩放效果代码时,控件内容会跟随窗体的拉伸,放大而进行适配,如下图所示
2.1、控件随窗体缩放适配思路
实现思路是:
①在窗体初始化时先获取窗体的宽度和高度,然后;
②遍历窗体控件进行初始化设置缩放位置;
③在窗体变化时获取当前窗体的宽度和高度,然后遍历窗体控件进行设置。
2.2、控件随窗体适配的核心代码
#region 控件大小随窗体大小等比例缩放
private readonly float x; //定义当前窗体的宽度
private readonly float y; //定义当前窗体的高度
private void setTag(Control cons)
{
foreach (Control con in cons.Controls)
{
con.Tag = con.Width + ";" + con.Height + ";" + con.Left + ";" + con.Top + ";" + con.Font.Size;
if (con.Controls.Count > 0) setTag(con);
}
}
private void setControls(float newx, float newy, Control cons)
{
//遍历窗体中的控件,重新设置控件的值
foreach (Control con in cons.Controls)
//获取控件的Tag属性值,并分割后存储字符串数组
if (con.Tag != null)
{
var mytag = con.Tag.ToString().Split(';');
//根据窗体缩放的比例确定控件的值
con.Width = Convert.ToInt32(Convert.ToSingle(mytag[0]) * newx); //宽度
con.Height = Convert.ToInt32(Convert.ToSingle(mytag[1]) * newy); //高度
con.Left = Convert.ToInt32(Convert.ToSingle(mytag[2]) * newx); //左边距
con.Top = Convert.ToInt32(Convert.ToSingle(mytag[3]) * newy); //顶边距
var currentSize = Convert.ToSingle(mytag[4]) * newy; //字体大小
if (currentSize > 0) con.Font = new Font(con.Font.Name, currentSize, con.Font.Style, con.Font.Unit);
con.Focus();
if (con.Controls.Count > 0) setControls(newx, newy, con);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 重置窗体布局
/// </summary>
private void ReWinformLayout()
{
var newx = Width / x;
var newy = Height / y;
setControls(newx, newy, this);
}
#endregion
三、使用方法
3.1、在窗体构造函数内初始化适配
//注意:UIComponetForm是自己需进行适配的窗体名称
public UIComponetForm()
{
InitializeComponent();
#region 初始化控件缩放
x = Width;
y = Height;
setTag(this);
#endregion
}
3.2、重置缩放布局
②选中事件,双击Resize即可生成重置窗口布局的基础代码
private void Form1_Resize(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//重置窗口布局
ReWinformLayout();
}
封装
是的,你可以将自适应布局的代码封装成一个单独的类或方法,以便在多个窗体中重复使用。以下是一个示例,演示如何将上述代码封装为一个可重用的类:
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Windows.Forms;
public class FormLayoutHelper
{
private float xRatio;
private float yRatio;
public FormLayoutHelper(Form form)
{
// 初始化窗体宽度和高度比例
xRatio = form.Width;
yRatio = form.Height;
SetTag(form);
}
private void SetTag(Control cons)
{
foreach (Control con in cons.Controls)
{
con.Tag = $"{con.Width};{con.Height};{con.Left};{con.Top};{con.Font.Size}";
if (con.Controls.Count > 0)
SetTag(con);
}
}
public void ResizeControls(Form form)
{
float newx = form.Width / xRatio;
float newy = form.Height / yRatio;
SetControls(newx, newy, form);
}
private void SetControls(float newx, float newy, Control cons)
{
foreach (Control con in cons.Controls)
{
if (con.Tag != null)
{
var mytag = con.Tag.ToString().Split(';');
con.Width = Convert.ToInt32(Convert.ToSingle(mytag[0]) * newx);
con.Height = Convert.ToInt32(Convert.ToSingle(mytag[1]) * newy);
con.Left = Convert.ToInt32(Convert.ToSingle(mytag[2]) * newx);
con.Top = Convert.ToInt32(Convert.ToSingle(mytag[3]) * newy);
var currentSize = Convert.ToSingle(mytag[4]) * newy;
if (currentSize > 0)
con.Font = new Font(con.Font.Name, currentSize, con.Font.Style, con.Font.Unit);
con.Focus();
if (con.Controls.Count > 0)
SetControls(newx, newy, con);
}
}
}
}
使用示例:
在你的 Form1 类中,可以像这样使用 FormLayoutHelper:
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
private FormLayoutHelper layoutHelper;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
layoutHelper = new FormLayoutHelper(this);
}
private void Form1_Resize(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
layoutHelper.ResizeControls(this);
}
}
这样,你就可以在多个窗体中使用 FormLayoutHelper 类来实现自适应布局,而不必在每个窗体中重复编写相同的代码。
封装2
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Windows.Forms;
public static class FormLayoutHelper
{
/// <summary>
/// 使窗体及其子控件自适应分辨率
/// </summary>
/// <param name="form">要自适应的窗体</param>
public static void EnableAdaptiveLayout(this Form form)
{
// 记录初始尺寸
form.Tag = $"{form.Width};{form.Height}";
// 保存初始布局信息
SaveControlLayout(form);
// 绑定Resize事件
form.Resize += (sender, e) =>
{
if (form.WindowState == FormWindowState.Minimized) return;
ResizeControls(form);
};
}
/// <summary>
/// 保存控件的布局信息到Tag属性
/// </summary>
private static void SaveControlLayout(Control control)
{
foreach (Control con in control.Controls)
{
con.Tag = $"{con.Width};{con.Height};{con.Left};{con.Top};{con.Font.Size}";
if (con.Controls.Count > 0)
SaveControlLayout(con);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 根据新的窗体尺寸调整控件大小和位置
/// </summary>
private static void ResizeControls(Control control)
{
// 获取初始尺寸
var originalSize = control.Tag.ToString().Split(';');
var originalWidth = Convert.ToSingle(originalSize[0]);
var originalHeight = Convert.ToSingle(originalSize[1]);
// 计算缩放比例
var newX = control.Width / originalWidth;
var newY = control.Height / originalHeight;
// 调整子控件
AdjustControls(newX, newY, control);
}
/// <summary>
/// 调整控件大小和位置
/// </summary>
private static void AdjustControls(float newX, float newY, Control cons)
{
foreach (Control con in cons.Controls)
{
if (con.Tag != null)
{
var mytag = con.Tag.ToString().Split(';');
con.Width = Convert.ToInt32(Convert.ToSingle(mytag[0]) * newX);
con.Height = Convert.ToInt32(Convert.ToSingle(mytag[1]) * newY);
con.Left = Convert.ToInt32(Convert.ToSingle(mytag[2]) * newX);
con.Top = Convert.ToInt32(Convert.ToSingle(mytag[3]) * newY);
var currentSize = Convert.ToSingle(mytag[4]) * newY;
if (currentSize > 0)
con.Font = new Font(con.Font.Name, currentSize, con.Font.Style, con.Font.Unit);
if (con.Controls.Count > 0)
AdjustControls(newX, newY, con);
}
}
}
}
使用方法:
在你的项目中添加这个
FormLayoutHelper类.在需要自适应的窗体的构造函数中调用
EnableAdaptiveLayout()方法:public partial class MyForm : Form { public MyForm() { InitializeComponent(); this.EnableAdaptiveLayout(); } }优点:
代码封装: 将自适应逻辑封装到一个单独的类中,提高了代码的可读性和可维护性。
易于使用: 只需要调用一个方法即可启用自适应布局。
递归处理: 可以处理嵌套的子控件。 注意:
该方法通过调整控件的大小和位置来实现自适应,可能不适用于所有布局场景。
对于复杂的布局,建议使用 TableLayoutPanel 或 FlowLayoutPanel 等控件来实现更好的自适应效果。
控件多 了容易卡顿
可以考虑使用定时器(Timer)或者异步操作来延迟执行布局调整,而不是每次 Resize 事件都立即调整布局 具体怎么实现, 加一种使用防抖来实现最后放下的鼠标时候才调整